Non performing asset
Updated on : 2020-Dec-05 04:12:25 | Author :
Introduction
A loan is called a “non-performing asset” when it is not being repaid by the borrower after talking the loan resulting in the asset no longer being able to generate income for the lender. It is because the interest is not being paid by the borrower. In this condition, the loan is considered “in arrears.” It is classified into four divisions. Here you can read more about NPA in detail.
Non- performing assets meaning
A loan is termed as a “non-performing asset” when it is not being repaid by the borrower after talking the loan resulting in the asset no longer being able to generate income for the lender. It is because the interest is not being paid by the borrower. In this condition, the loan is considered “in arrears.”
Classification of NPA
The Lenders generally provide a grace period before making the process of classifying an asset as a “non-performing” one. Afterward, the lender may be the bank will categorize the NPA into some sub-categories mentioned below in details:
1. Standard Assets
The standard assets classification of the NPAs that have been past due from anywhere from 90 days to 12 months with a normal risk level.
2. Sub-Standard Assets
Sub-standard assets are the NPAs that have been past due for more than 12 months. They possess a significantly higher risk level that is combined with a borrower. That has less than ideal credit.
3. Doubtful Debts
The Non-performing assets in this category like past due for at least 18 months. Banks generally have doubts that the borrowers will ever repay the full loan or they will not. This category of NPA actually affects the bank’s own risk profiles.
4. Loss Assets
These are also non-performing assets having an extended period of non-payment. With this class, the banks are forced to accept that the loan will never be repaid. It must record a loss on their balance sheet. The entire loan amount must be written off completely.
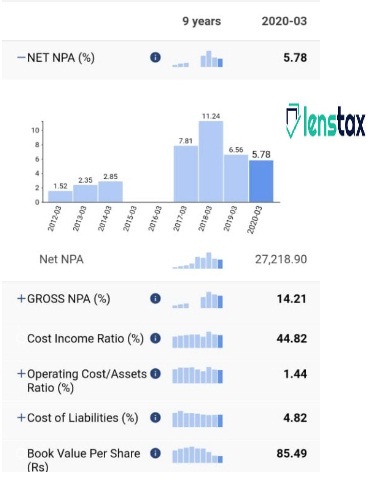
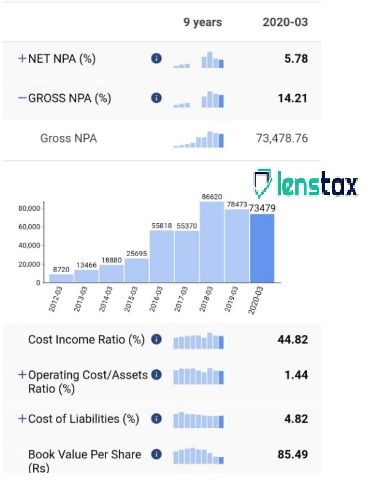
Gross NPA and Net NPA
Gross non-performing assets are the sum of all the loans which have been defaulted by the borrowers within the specific provided period. The net non-performing assets are the amount resulting after the deduction provision for the unpaid debts from gross NPA.
Gross NPA suggests the Gross Non-Performing Assets. The commercial banks use Gross NPA is the term. It refers to the sum of any unpaid debt, which is classified as non-performing loans or assets. These Commercial banks offer loans to the non-honored customers, and the financial institutions are also required to classify them as non-performing assets within 90 days time period as they don’t receive the main amount or net payments.
Net NPA is Net Non-Performing Assets. It is used by the commercial banks to indicate less allowance for the poor and uncertain debts than the non-performing loan amounts. To cover the unpaid debts, the commercial banks tend to offer the precautionary amount. Hence, in case one deducts this provision for the unpaid loans from the unpaid obligations. It results in the sum relates to the net non-performing assets.
The differences between the Gross NPA and Net NPA:
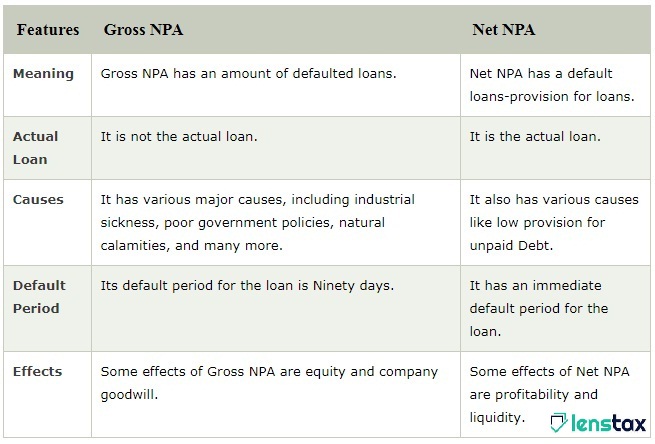
- Gross NPA is the entire amount of the debts. It I have not been collected by an organization or the individuals owing the organization has not fulfilled their obligations of the contract to pay both the amount of the principal and also the interest. Besides, the net non-performing loan is the amount that results from the sum of the defaulted loans after the deduction of the provision for the uncertain and unpaid debts. It is really a loss that the organization incurs after defaulted loans.
- Credit institutions have a grace time period during which an individual starts paying for the loan and its interests. When the term payout expires, the institution is advised to write off the debts which are not paid. But after ninety days period, the non-performing loans are classified as default and these are accepted globally. Any kind of payment due after the grace period of ninety days is termed as a default.
- Gross NPA = (A1 + A2 + A3 ……………………. + An)/Gross Advances, where A1 is the person who has taken the loans. The net NPA is the sum that is realized after the amount has been deducted from the overall NPAs.
- The Net NPA is calculated as= (Total Gross NPA) - (Provision for Unpaid Debts)/Gross Advances
- Some significant causes of gross non-performing assets are weak government policies, willful defaults, the unsuccessful recovery court, industrial disease, natural disasters, and many others. While net NPAs are the main products of gross non-performing assets.
- Another difference between the gross NPAs and the net NPAs is the actual loss the corporation refers to as the companies.
​​​​​​​
- A negative impact on the corporation's reputation and a negative impact on the enterprise's equity valuation.


